Main Screen
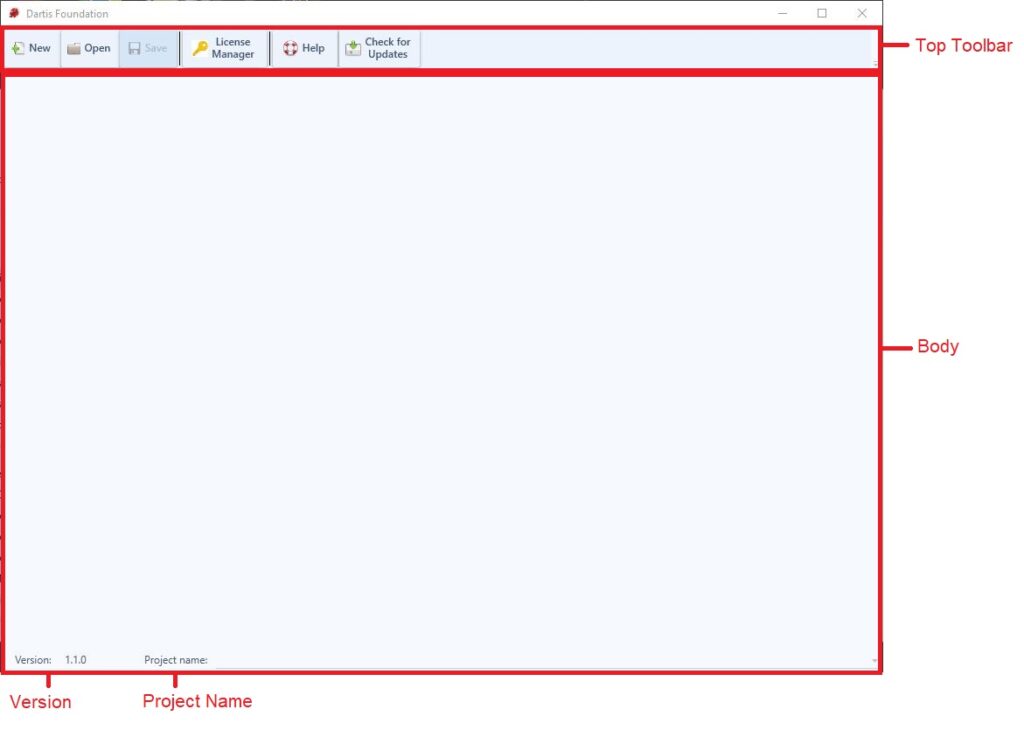
This is the screen encountered when opening the program.
Top Toolbar
The toolbar provides you the access to create/load/save projects, license information, help file, etc.
In the first application run, create a “New” project. This provides you with the tab control to work with.
To open a previously created project, click on “Open” button and choose the saved .DFo file on your local hard drive.
Click on “Save” button to save changes in your project. Make sure you save your data periodically.
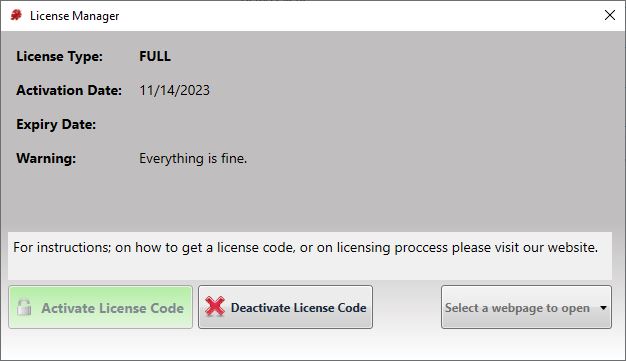
The License Manager page includes the current license information. it also allows you to activate a new license (e.g. to upgrade from Evaluation / Trial Version to Registered Version) or to de-activate the license on this computer. Click on License Manager button to open the License Manager page.
“Help” button opens help manual.
“Check for Updates” button checks online for available updates.
Project Information
Basic project information including name, client, location, company info. and project No. are entered in this section. This data will be shown in the fine calculations report.
Soil Layers
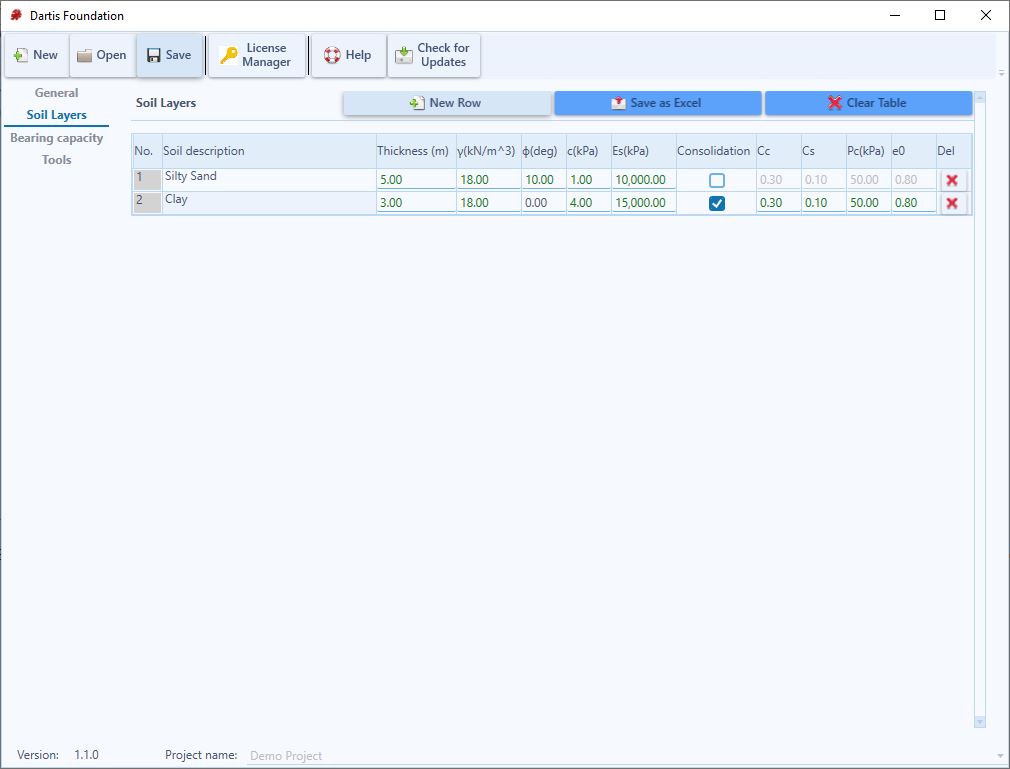
Your stratigraphy model may contain unlimited soil layers. Please specify the following parameters for each layer:
- Soil Description: simple description for layer. This field is only for user’s information and does not have any effect on bearing capacity analysis
- Thickness: thickness of the layer.
- γ: Total unit weight.
- φ (deg): Internal angle of friction (between zero and 45 degrees).
- C: Coefficient of cohesion.
- Es: Modulus of elasticity.
- Consolidation: determines whether consolidation settlements are calculated or not.
- Cc , Cs: Consolidation compression and re-compression indexes. They should only be entered when you want the consolidation settlement to be calculated for this layer.
- Pc: Pre-consolidation stress for consolidation settlement.
- eo: Void ratio.
New Row: Inserts a new soil layer.
Save as Excel: Exports Soil Layers table to Excel (You need to have Excel installed on your PC).
Clear Table: Removes all soil layers.
Bearing Capacity
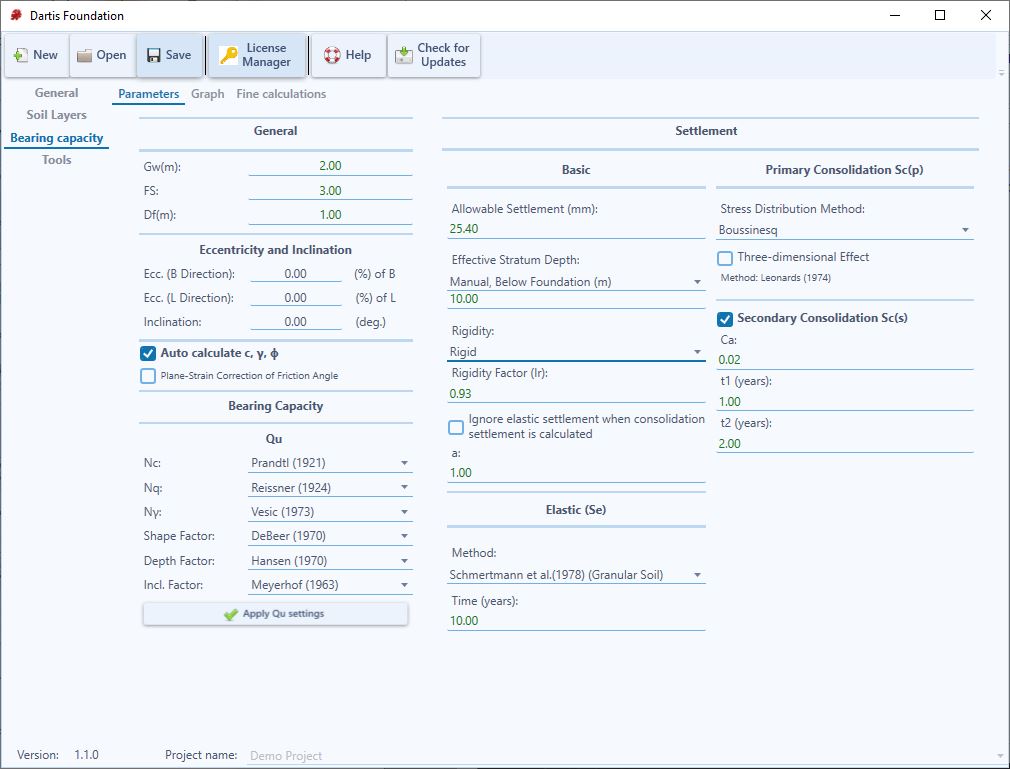
_General
- Gw: Depth to water table measured from the ground surface.
- FS: Factor of safety. The allowable bearing capacity based on shear failure is obtained by dividing the ultimate bearing capacity by the factor of safety.
- Df: depth of footing base measured from the ground surface.
_Eccentricity and Inclination
- Ecc. in B & L Directions: Load eccentricity in footing’s width and length directions expressed as percentage.
- Inclination: Inclination of the load on the foundation with respect to the vertical.
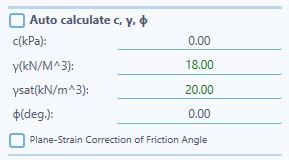
_Auto calculate c, φ, γ: If checked the parameters are calculated based on soil layers information. Uncheck to insert manually as shown in figure below:
_Plain-Strain Correction of Friction Angle: Meyerhof (1963) suggested the following equation to interpolate the friction angle for rectangular foundations:
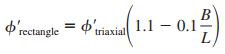
The bearing capacity factors Nc, Nq, and Nγ are very sensitive to the friction angle. Therefore, it is necessary to select the appropriate friction angle.
_Bearing Capacity
__Qu
Choose calculation method for each factor and click on “Apply Qu settings”.
_Settlement
__Basic
Allowable settlement: In order to control the settlement of the footing and its superstructure, the allowable settlement (sum of elastic and consolidation settlements) is limited to this value.
Effective stratum depth: Effective depth in settlement calculation is determined by each of the following criteria:
- Multiple of footing width – xB: Effective stratum depth is considered equal to an optional multiple of footing width.
- Manual, Below Foundation: Effective stratum depth is considered at the specific depth.
Rigidity: Two footing types, flexible and rigid are available. Rigidity factor (Ir) is less than one and depends on rigidity of the footing (usually 0.9 to 1). Dartis Foundation applies this factor to the total settlement of the footing S=(Se+Sc)*Ir where Se and Sc are elastic and consolidation settlements, respectively. For flexible footing this factor is one.
Ignore Elastic settlement when Consolidation settlement is calculated: If marked, Elastic settlement is ignored when there is a soil layer with consolidation settlement.
a: this factor is used for calculation of un-saturated consolidation settlement. If a fine-grained layer is unsaturated (e.g. S=80%), then the actual consolidation settlement is a fraction of calculated saturated consolidation settlement.
__Elastic (Se)
Method: Three methods can be chosen for elastic (immediate) settlement calculation of footings. For further reference and detailed description of each methodology please refer to reference books.
__Primary Consolidation (Sc(p))
Stress Distribution Method: Two methods are available; Boussinesq and approximate 2V:1H. Calculations are performed in top, middle and bottom of the layer and the result is obtained by the use of Simpson’s rule.
Three-dimensional Effect: Leonards (1976) examined the correction factor Kcr for a three-dimensional consolidation effect in the field for a circular foundation located over overconsolidated clay. The interpolated values of Kcr(OC) from Leonard’s 1976 work are given below:
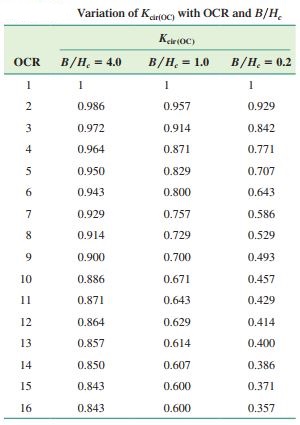
B = Foundation width
Hc = Effective stratum depth
__Secondary Consolidation (Sc(s))
Ca = secondary compression index.
t1, t2 = time.
Graph
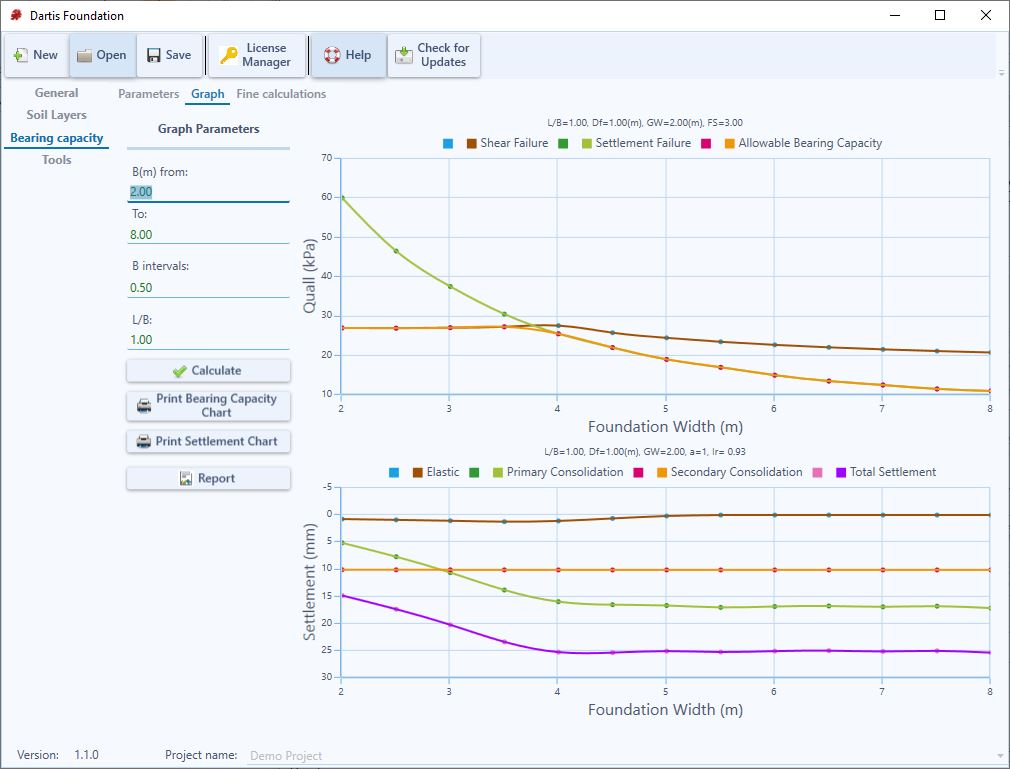
Dartis Foundation calculates both shear failure and settlement criteria for a range of footing widths (i.e. B1 to B2). At each footing size:
1. Shear Failure (Brown Curve): The allowable bearing pressure based on shear failure is calculated.
2. Settlement Failure (Green Curve): This curve shows the allowable stress, provided that the total settlement is around the allowable settlement already introduced by the user.
Allowable Bearing Capacity Curve (Orange Curve): This curve is the lower intersection of two above-mentioned curves and assures that on each point along the curve, both settlement and shear failures are within the allowable limits.
_Settlement Graph: This includes 4 curves representing Immediate (elastic), Primary Consolidation, Secondary Consolidation and Total settlements. Please be advised that these settlement values are calculated based
on the resulting allowable bearing capacity calculated for each specific footing size.
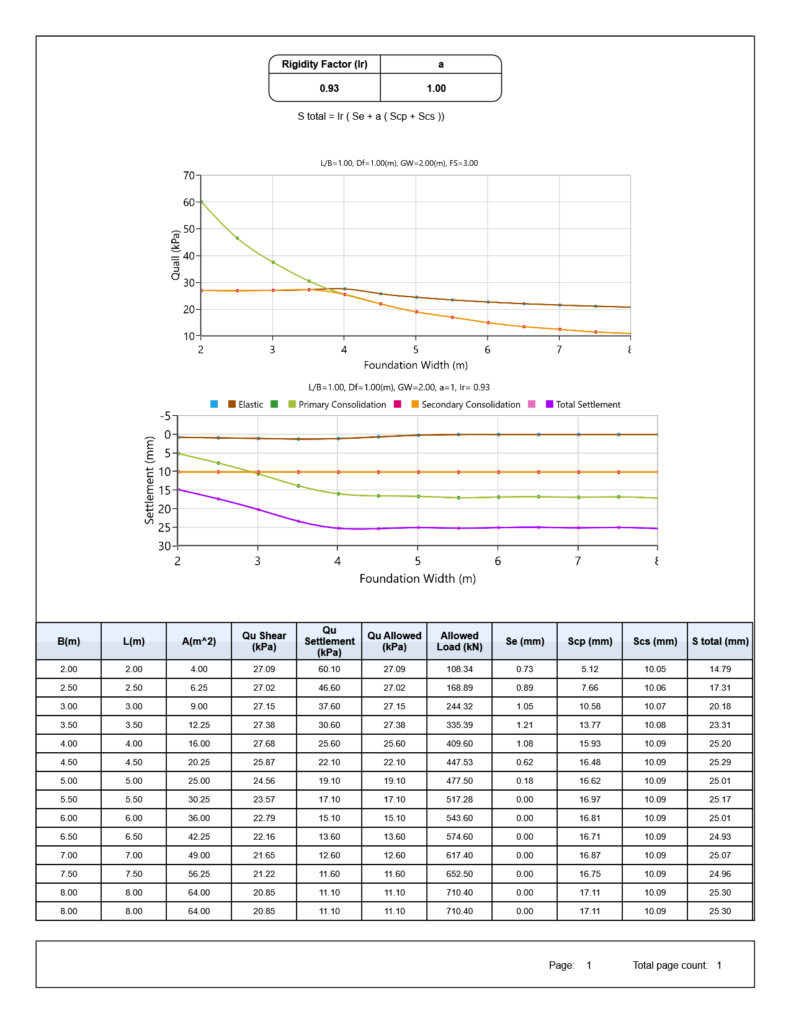
_Graph Report: Click on “Report” button. Image below is an example report of this page saved as .Png. This report can be saved as Word, Excel, Image, etc.
Bearing Capacity and Settlement graphs can also be printed separately.
Fine Calculations
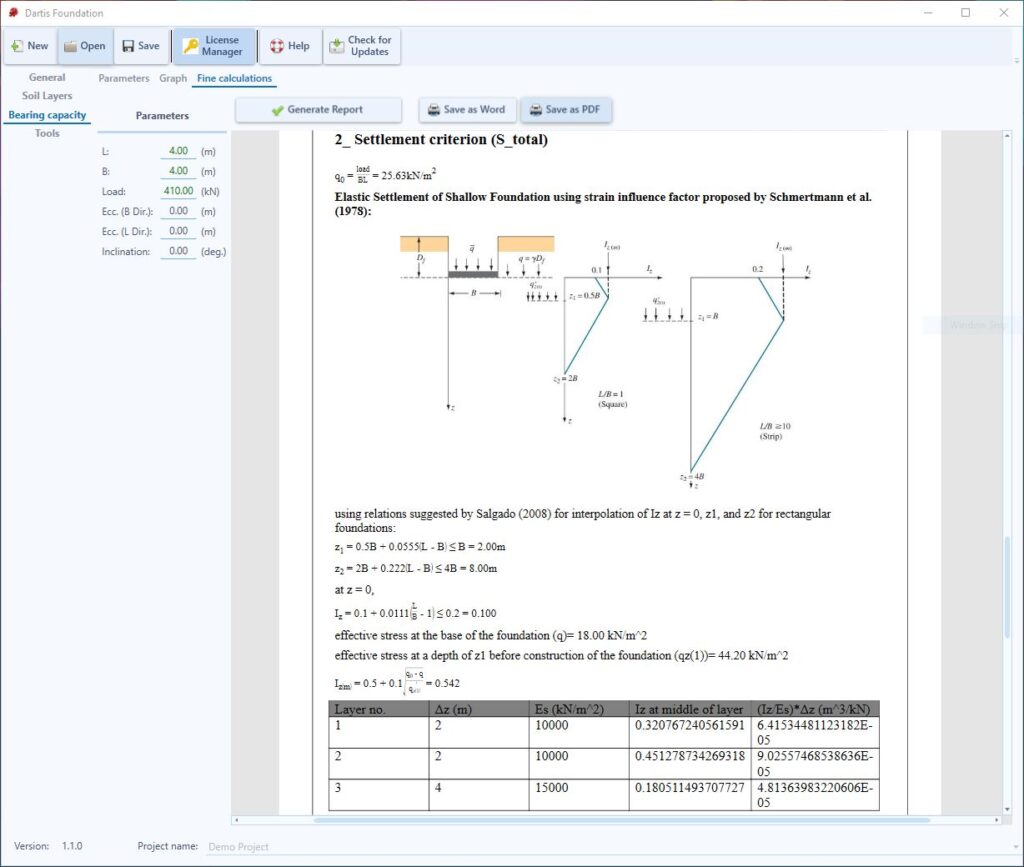
In this section fine calculation report is generated based on parameters introduced by user.
This is a full detailed report including formulas, considerations, methods, etc. This report can be exported as Word and PDF formats.



