Table of Contents
Grain Size Analysis
Soils can be classified from different points of view, such as the size of grains or the type of minerals, or from their resistance and origin.
In general, it can be stated that many of the mechanical and physical properties of soils are a function of the type, shape, size and distribution of grain size. On this basis, the basis of the engineering classification of soils, their size and pasty properties are placed. Almost all classification systems divide soils into three categories: coarse-grained (non-sticky), fine-grained (sticky) and organic soils.
In these classifications, grain means a single mineral particle or a piece of several minerals connected together that will not be separated from each other in water. Soil grain size test is one of the important soil tests that is performed according to the ASTMD422-63 standard. The soil grain size test is usually done in three main ways that depend on the size of the soil particles.
The first method:
Soil grain size test by sieve method can be used mainly for soil that has more than 90% of grains larger than sieve number 200.

The second method:
For soils with more than 90% of grains smaller than sieve number 200, hydrometric soil mechanics test is used for soil grading.
The third method:
It can be used for soils that do not belong to any of the other two categories and are so-called mixed . So that in this method, a combination of both soil sieve and hydrometry tests are used for soil classification. hydrometer tests will be used for the fine-grained part of the soil, and soil grain size tests using the sieve method will be used for the coarse-grained part of the soil.
Application of soil grain size test by sieve method
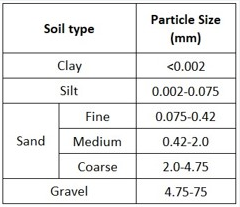
In order to express the application of soil grain size testing using the sieve method, it can be mentioned that many mechanical and physical properties of soil are dependent on the size, shape, type and distribution of grains, and this distribution of grains leads to the naming according to The table is below.
Equipment required for sieve method
Soil grain size test by sieve method requires the following equipment, the most common of which are as follows:
scale:
The scales that are used for testing materials and soil grading and hydrometer test must have the following accuracy:
1. In order to perform grain size and hydrometer test of fine-grained materials, the accuracy of the scale must be 0.1 grams or 0.1% of the tested materials (whichever is greater).
2. In order to perform grain size and hydrometer test of fine-grained and coarse-grained materials, the accuracy of the scale must be 0.5 grams or 0.1% of the tested materials (whichever is greater)
Sieve:
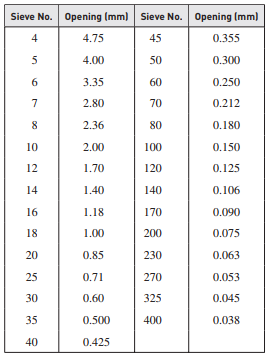
1. Sieves for conducting soil grain size test should be mounted on each other in such a way as to prevent the waste of materials during sieving.
2. Sieves to perform soil grain size test by sieve method must have the specifications mentioned in ASTM E11 .
3. Variations in the average spring diameter of sieves that are larger than 125 mm (5 inches) can be ±2% and the nominal diameter of sieve wire should be considered 8 mm or larger.
Mechanical sieve shaker (shaker):
The mechanical shaker of the sieve transmits vertical vibration or lateral vibration to the soil granulation sieve, this vibration should be applied in such a way that the grains jump up and down and slide on the sieve surface in different directions. And they can be classified in the next steps according to the presence of grains in each sieve.
Oven:
In order to conduct the soil grain size test using the sieve method, it is necessary to use an oven with a suitable size that can maintain a uniform temperature of 110 ± 5 degrees Celsius (230 ± 9 degrees Fahrenheit).


Sampling of soil grain size test by sieve method:
The weight of the sample that is used for testing soil grain size distribution should be approximately equal to the desired weight after drying. Also, in the test of soil grain size using the sieve method, the amount of sample required for coarse grain mixtures is such that it is possible to perform the test with mechanical vibrators. The result of the mechanical soil grain size test for samples of aggregates larger than 50 mm is also satisfactory, provided that the amount of the sample is small and the acceptance or non-acceptance criterion of the material is the average of the results of several tests.
The method of conducting soil grain size test by sieve method
In the first step of the soil granulation test by sieve method, it is necessary to dry the test sample at a temperature of 110 ± 5 degrees Celsius (230 ± 9 degrees Fahrenheit) until reaching a constant weight. Then the sieves are placed on top of each other in order of number, from big to small and from top to bottom, and the soil sample is poured on the top sieve. It should be noted that the sieves will be slid by hand or with the help of a mechanical slider for a sufficient time.
In the next step of testing soil grain size using the sieve method, it is necessary to limit the amount of material on the sieve to such an extent that all the grains have the opportunity to be exposed to the holes of the sieve several times. For sieves whose spring is smaller than 4.75 mm (number 4), the weight of the material remaining on the sieve should not exceed 6 kg per square meter (4 grams per square inch) of the sieve surface. Also, in the soil grain size test, sieves which springs are 4.75 mm (number 4) or larger, the weight of the material on the sieve in kilograms per square meter must not be more than 2.5 times the size of the sieve holes (in millimeters m).
It should be noted that in the test of soil grain size using the sieve method, the weight of the material should not be placed on the sieve to such an extent that the texture of the sieve changes its shape permanently.
Be careful, in the mechanical soil grain size test, sieving will continue until less than one percent of the weight of the material remaining on each sieve passes through it for every one minute of sieving.
During soil graine size test, a part of the sample that is finer than 4.75 mm (No. 4) can be distributed on two or more series of sieves to prevent excessive accumulation of materials on the sieve.
Finally, the weight of the material left on each sieve is determined with a scale with an accuracy of 0.1% of the initial dry sample weight. Also, during the testing of soil grain size using the sieving method, it is necessary to check the total weight of the material after sieving with the initial weight of the sample, and if the difference between the two is more than 0.3%, the results are not acceptable.
The work report of soil grain size test by sieve method
Depending on the required specifications of the materials under soil grain size testing, the soil granulation report should include the following:
The percentage of the total material passed through each sieve.
Percentage of total material remaining on each sieve.
- The percentage of materials remaining between successive sieves.
Hydrometer test
Hydrometric analysis is performed to evaluate the size distribution curve of fine soil grains (generally smaller than 75 micrometers), which cannot be classified by mechanical sieving due to their small size.
It should be noted that the results of soil mechanics hydrometer tests are not used to classify soils, but to obtain information about the engineering behavior of fine soil grains
Hydrometer test theory
Heisen relations are used to estimate soil hydraulic conductivity. Hydrometer testing is based on the fact that Stokes’ law has the ability to be used for the precipitation of fine soil grains. Stokes law describes the deposition process of spherical grains that do not interact with each other.
hydrometer test equipment
1. Electric mixer.
2. Hydrometer.
3. A solution that separates soil particles from each other.
4. Distilled water.
5. Sodium hexametaphosphate.
6. Thermometer with half degree centigrade accuracy.
7. Sedimentation Cylinder and witness cylinder.
8. Timer (chronometer).
9. Standard sieve No. 10 with sieve head and pan.
How to conduct hydrometer test on soil
1. To perform hydrometer test, we use 50 grams of soil passed through sieve No. 10, weighed by a digital scale (with an accuracy of 0.1 grams).
2. In the hydrometer test of soil, a separating solution with a concentration of 40 grams of NaPO3 sodium hexametaphosphate powder is prepared in 1 liter of distilled water, and then 125 cc of the separating solution is mixed with 50 grams of soil passed through sieve No. 10 inside the mixing bowl for 5 It is mixed with a mixer for 10 minutes.
3. According to ASTM D422-6, the soil should be soaked in the solution for 16 hours. But in the laboratory, due to the lack of time, they may not allocate such time to wet the soil, so the solution is mixed again for 5 to 10 minutes.
4. In the next step of hydrometer test, after the volume of the solution with distilled water is 1000 ml, we bring the temperature of the solution to a constant temperature using a hot water bath with a constant temperature, of course if the temperature is 20 degrees Celsius. degrees, there is no need to apply the temperature correction factor.
5. In this step of hydrometer test and after stabilizing the temperature with a plastic cap, the cylinder is upside down for one minute and at least fifty times. Then the graduated cylinder is placed in a completely fixed position and the first reading is taken immediately using the hydrometer. But the next readings are done at 0.5, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 15, 30, 60, 250 and 1440 minutes.
Limitations of soil hydrometer test
Hydrometer testing of soil has two important limitations:
- The first limitation of hydrometer testing is the assumption that grains do not interact with each other. This assumption is not correct especially for clays because the electric charge on the surface of the clays will cause attraction and electric repulsion forces between adjacent grains.
- The second limitation of hydrometer test is that the clay grains are not spherical but can be seen as plates or needles. Therefore, the hydrometer test for clay grains is not accurate and will be a part of the approximations of the hydrometer test. In addition, hydrometer testing of soil is not performed by measuring the time and distance of fall for each particle, but instead, the temporal changes in the density of the soil solution slurry will be measured. As the soil grains settle inside a cylindrical cylinder, the density of the slurry of the soil solution will decrease and the hydrometer inside the solution will sink down.
Modification of hydrometer test
The corrections required for hydrometric testing of soil mechanics not only include corrections of crescent, heat and density, but also corrections of geometry, crystal volume and cross-sectional area of sediment cylinder.
The cost of hydrometer test
grain size test and hydrometer test of soil is one of the important and vital soil tests to measure the dimensional distribution of the soil, which is used mainly regardless of the cost and price of the test to measure the soil dimensions. But in general, the cost of grain size and hydrometer test of soil is different according to the type of soil.
You may also want to read our article about soil testing.